| ||||
African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of StatesWikipedia short informationThe African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP) is a group of countries in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific that was created by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975. The group's main objectives are sustainable development and poverty reduction within its member states, as well as their greater integration into the world's economy. All of the member states, except Cuba, are signatories to the Cotonou Agreement with the European Union. The Cotonou Agreement (signed in Cotonou, Benin in June 2000) is the successor to the Lomé Conventions. One of the major differences from the Lomé Convention is that the partnership is extended to new actors such as civil society, private sector, trade unions and local authorities. These will be involved in consultations and planning of national development strategies, provided with access to financial resources and involved in the implementation of programmes. Many small island developing states are ACP states; the fourth Lomé Convention was revised in 1995 in Mauritius and gives special attention to island countries in this agreement. Link: ACP
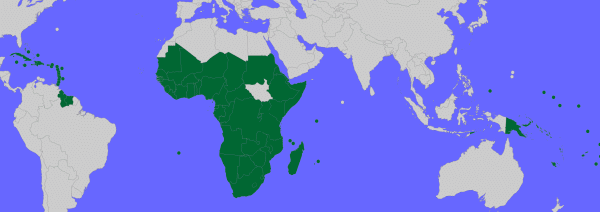
Members, Observers and other participations
| ||||
|




