|
|
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM) is an organization of fifteen Caribbean nations and dependencies whose main objective is to promote economic integration and cooperation among its members, to ensure that the benefits of integration are equitably shared, and to coordinate foreign policy. The organization was established in 1973. Its major activities involve coordinating economic policies and development planning; devising and instituting special projects for the less-developed countries within its jurisdiction; operating as a regional single market for many of its members (Caricom Single Market); and handling regional trade disputes. The secretariat headquarters is in Georgetown, Guyana. CARICOM is an official United Nations Observer. Established mainly by the English-speaking parts of the Caribbean, CARICOM has become multilingual in practice with the addition of Dutch-speaking Suriname on 4 July 1995 and French- (and Haitian Kreyòl-) speaking Haiti on 2 July 2002. Furthermore, it was suggested that Spanish should also become a working language. In July 2012, CARICOM announced that they were considering making French and Dutch official languages. In 2001, the heads of government signed a revised Treaty of Chaguaramas that cleared the way to transform the idea of a common market CARICOM into a Caribbean (CARICOM) Single Market and Economy. Part of the revised treaty establishes and implements the Caribbean Court of Justice. Link: CARICOM
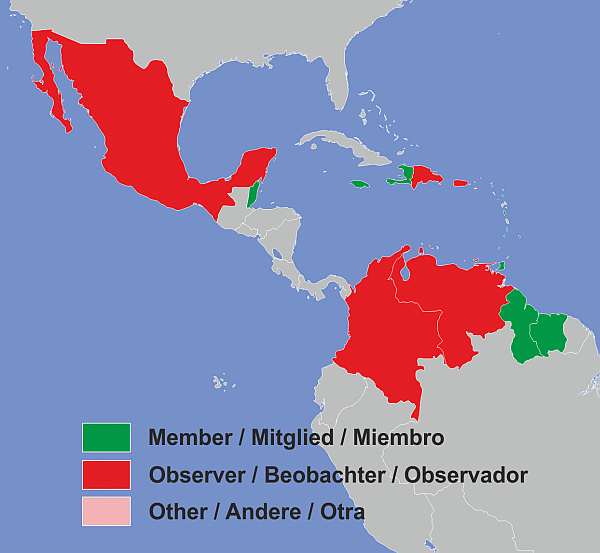
Members, Observers and other participations
|
|
