| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gulf Cooperation CouncilWikipedia short informationThe Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, originally (and still colloquially) known as the Gulf Cooperation Council, is a regional intergovernmental political and economic union consisting of all Arab states of the Persian Gulf, except for Iraq. Its member states are Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The Charter of the Gulf Cooperation Council was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution. All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain), two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir). There have been discussions regarding the future membership of Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen. A 2011 proposal to transform the GCC into a "Gulf Union" with tighter economic, political and military coordination has been advanced by Saudi Arabia, a move meant to counterbalance the Iranian influence in the region. Objections have been raised against the proposal by other countries. In 2014, Bahrain prime minister Khalifa bin Salman Al Khalifa said that current events in the region highlighted the importance of the proposal. In order to reduce their dependence on oil in the future, the GCC states are pursuing unprecedented structural reform initiatives. Link: GCC
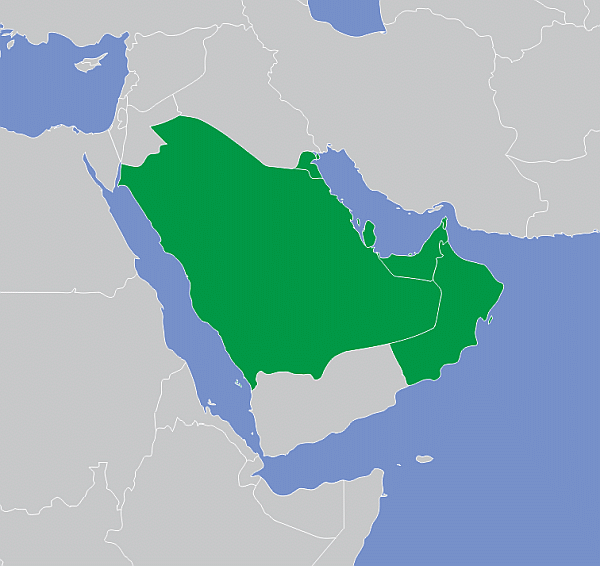
Members, Observers and other participations
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|




